DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ††
The system with deals with digestion of food with process of metabolism is called digestive system.
- Ingestion - Intake of food.
- Assimilation - Mixing of food.
- Digestion - Digestion of food.
- Secrtion - Making of juice.
- Absorption - Absorb of food.
- Egestion ( excreation) - excreate of stool.
:: ABDOMINAL REGION ::
a) Right hypochondriac region - Liver, Gallbladder.
b) Epigastric region - Stomach, Body of pancreas.
c) Left Hypochondriac regions - Tell of pancreas, spleen.
d) Right lumber regions - Right kidney, Right adrenal glands.
e) Umbillical regions - Head of pancreas, Small intestine.
f) Left Lumber regions - Left kidney, left adrenal glands.
g) Right Iliac fossa - Vermiform appendix, Right urethra.
h) Hypo gastric region - Urinary bledder male and female reproductive organs.
i) Left Iliac regions - Left uretor, colon.
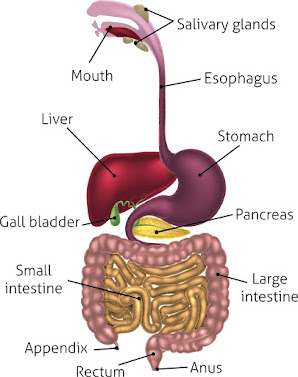
::: Accessory organs of the digestive :::
Mouth (Oral cavity)*
The walls of the oral cavity are formed by.
Anterior : lips and teeth
Posterior : Pharynx
Superior : Hard palette
Inferior : Tongue and soft tissue
Lateral : Muscles of the cheeks and teeth.
Tongue ( lingual )*
It is made up of voluntary muscles and attached to hyoid bone at the base. Taste buds are present all over the tongue
Blood supply - tongue is supplied by-
Lingual artery a branch of external carotid artery. The lingual vein joins The internal jugular vein.
SALIVARY GLAND (RECEMOSE GLAND)
There are three part of salivary gland. These gland pair their secration into mouth cavity.
(A) Parotid gland (Discovered by "Wharton's Duct")
These are located just below the external auditory meatus one each side. The duct carrying saliva from these glands open into the mouth cavity at the level of the upper second moler tooth.
(B) Sub Mandible Gland ( discovered by"Stemen Duct")
These are situated one on each side under the angle of the how. The ducts from these gland open on the floor of the mouth.
(C) Sub Lingual Gland
These gland lie under the mucus membrane of the floor of mouth in front of the sub lingual glands. There are many small duct from these glands that open into the floor of the mouth.
The composition of Saliva ::
The saliva is composed of water, mucous, enzyme, minerals salts, lysozyme, blood clotting factor, sand immune globulines.
Function of saliva ::
- Digestion of carbohydrates.
- Salivary amylase will breakdown complex polysaccherides into maltose.
- Cleaning of lubricating.
- Non specific defense by lysozyme, immune globulins.
- Taste - When the dry food get mixed with saliva then only there will be a sense of taste.
PHARYNX (Throat)::
It is divided into three part.
A. Nasopharynx.
B. Oropharynx
C. Laryngopharynx
The nasopharynx is important in respiration. The oropharynx is common for respiration and digestion.
The mucosa is made up of satisfied squamous epithelium the middle layer consists blood vessels, lymphs vessels and nerves.
The outer layer consists of involuntary muscles which help swallowing .
The nerve supply is form vagus nerve and glassopharyngeal nerve ( parasympathetic) and cervical ganglia ( sympathetic).
ESOPHAGUS ( Good pipe )
It is tubular organ. It is 25 cm long and 2 cm in diameter. In thorax it lies in the midline in front of vertebral column and behind trachea and heart. It passes through diaphragm at the level of 10th thorasic vertebra. It end at the cardiac orifice of stomach in abdomen. The esophagus has same four layers else where seen in alimentary canal from outside the layer are --
1) Fibrous outer layer composed of fibrous connective tissue.
2) Muscular layer is made up of outer longitudinal and inner circular.
3) Sub mucosa areolar tissue with blood vessels lymphatic vessels nerves.
4) Mucosa - The mucus membrane secrets mucus. The upper two thirds of the esophagus are made up of sreriated volumetary muscles and lower one third is formed by involuntary smooth muscles. The vagus nerve supplied nerve fibers to the esophagus. In peristalsis ( mucus movement) the dilutions is followed by contractions which the 9 sec to pass the bolus of food from the pharynx to the stomach.
Function of Oesophagus, pharynx and mouth-------
1) Bolus formation
2) Deglutition ( swallowing )
3) Transport of food
::: STOMACH :::
The stomach is a 'J' shaped situated in epigastric umbilical and hypochondriac region. The stomach has two orifices proximal one is called cardiac and distal one is called pyloric. The ' J' shaped organ has got two curvatures, one right border is lesser curvature. Stomach is divided into three parts upper one is called fudus, middle part is body and lower part is called pylorous. The capicity. The capicity of the stomach is 1500ml in adult
The important organs associated with stomach are ----
1) Anterior - Liver and abdominal wall.
2) Posterior - Aorta pancreas, left adreanal, spleen, kidney ( left )
3) Superior - Diaphragm
4) Inferior - Transverse colon and small intestine
5) To the left - Diaphragm and spleen
6) To the right - Liver and duodenum
Wall of the stomach -----
It is formed by layers like other in alimentary canal
- Muscles layer
- Mucosa
- Sub mucosa
- Peritoneum
1) Muscles layer :
a) Inner -- oblique
b) Middle -- Circular
c) Outer -- longitudinal
2) Mucosa :
In this layer there are two types of gastric glands. They secreate enzyme and hydrochloric acis when stomach is empty mucus membrane is thrown into folds called reggae.
3) Sub mucosa :
It is made up of loose connective tissue
4) Peritoneum :
Outer most layer is made up of loose fibrous connective tissue.
:::: SMALL INTESTINE ::::
- The small intestine is continuous with the stomach at the pyloric sphincter and joins large intestine at the leo caeccal junction. It is more than 5 cm in length. It lies in abdominal cavity and surrounded by large intestine.



Comments
Post a Comment