- BONE : Bone is a connective tissue. It is made up of osteocytes. The cells are surrounding by collagen fibers with deposits of inorganic salts especially calcium and phosphates.
- Long - femur Tibia, fibula, Humerus, Radius.
- Short : Carpals, Metacarpals, Torsol, Earbone.
- Irregular : Vertebrae e skull
- Flat : Sternum and skull
- Sesamoid : Patella ( knee cap - It is present in tendon of Quadriceps - thig muscles )
- It maintain the structure and shape of body.
- It protect the internal organs.
- It helps movement and locomotions.
Classification of Joints
- T.M. joint{Temporal + mendiable}
- Shoulders {Scopulla+ Calavicle+ humerus}
- Elbow {Radius + Ulna+ humerus}
- Wrist {Radius+ Ulna+ Carpal}
- Knee {Femur+ Tibia+ Fibulate+ patella}
- Hip {Inominate+ Femur}
- Ankle {Torsal+ Tibia+ fibulla}
- Immoveable Joints
- Slightly moveable joints
- Free moveable joints
Skull bones, frontal bones, occipital, temparal, parietal
Slightly moveable
Knee joints, elbow joints, T.M. joints
Free Moveable Joints
A. Ball socket: Shoulder joints, Hip joints
B. Hinge ( spring): Ankle joint, wrist joints, Invitable joint
C. Pivot (point joint): elbow joint, T.M. joints
D. Saddle(♎): knee joint, thuria joint,
E. plano concave : Straight, phaleger joints, radiovlna joints
Function of Joints
- It maintain the structure and shape of body.
- It protect the internal organs.
- It helps movement and locomotion.
Muscles are made up to group of tissue the study of muscles are called Miology.
Muscles are present in male - 765
Life spoom of muscles in 65 days.
Types Of muscles
- Valuntary muscles : Which muscles whose are control in our body. E.g. Hand muscles.
- Involuntary muscles : Which are not controlled in our body. E.g. Urinal muscles.
- Ear :Lateral, Medial, Supra orbital, Infra orbital muscles.
- Face : Facial muscles.
- Lips : Orbicularis muscles, Orbioiloris muscles.
- Smile : Buccinator muscles.
- Depresser : Orbiculoris angularis (Corner).
- Neck movement : Sternoeleideid.
- Chewing : Masselar muscles.
- Chest : Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor muscles.
- Hands : Deltoid, Biceps, Triceps muscles.
- Palm : Hypothener, Respiratory, Abdominal muscles.
- Buttok : Gluteus maxis, Gmdius, Gminimus muscles.
- Back muscles : Psoas muscles.
- Thigh : Hamstring, Quadriceps muscles.
- Back thigh : Popliteal muscles.
- Calves muscles : Soleus, Gastronemics muscles.
- Leg sole muscles :Planter muscles
- Humerus muscles : Flexor muscles ( fold).
- Hand outside : Abductor muscles.
- Hand inside : Adductor muscles.
- Hand open muscles: Extensor
Where as same group of muscles are become short in size and there are attached each other to form a tendons. Every muscles two there work by controlling and relaxing of the muscles.
Chemical Substance
- Actin - Contraction
- Mysine - Relaxation
Function of muscles
- It maintain the structure and shape in the body.
- It protect the internal organs.
- It helps movement and locomotions.
The vertebral column is made up of 33 vertebrae. These are irregular shaped bones they are firmly connected to each other. These vertebrae together from a column which has limited movement
The cervical (Neck) and lumber part can move more freely then thoracic part and sacral part. The size, shape and other features of a vertebrae very form part is vertebral column.
A typical vertebrae has got a body pedicals formen transverse process.
There are five parts in a spinal cord ( regions)
- 7 cervical
- 12 thoracic
- 5 limber
- 1 secral (5 fused vertebrae)
- 1 coccyx ( 4 fused vertebrae)
::VERTEBRAL COLUMN ::STRUCTURE
Ligament of vertebral column
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Transverse longitudinal ligament
- Posterior longitudinal ligament
Function of the vertebral column
- Protection of spinal cord.
- Protection of spinal nerves. Blood vessels and lymph vessels.
- Support the skull.
- Attachment the ribs. And shoulder pelvis.
- Shock absorption and brain protection.
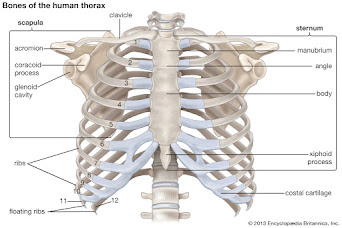
Thoracic Cage :
The bones of thoracic cage are ribs (12 pairs), sternum (1 pair: breast bone) and thoracic vertebrae (12 pair).
:: RIBS ::
The ribs form the anterior and lateral wall of the chest cavity with thoracic vertebrae in the back. The superior 10 pair join sternum by costal cartilages.
The last ( inferior) two pairs are free and called floating ribs.
The head of a rib articulate with the bodies of two adjacent thoracic vertebrae. The anterior end of a rib is attached to the sternum by costal cartilage ( elastic and hyoline) the space between the two ribs is filled by the inter costal muscles.
During inspiration the muscles content and increase the capicty of the thoracic cavity by lifting the ribs and sternum up words and outwords.

Hay
ReplyDelete